Are you experiencing wrist pain? Does repetitive use cause your pain? This type of injury is common, especially from computer keyboarding and mouse use. Often, a few simple strategies and exercises are all it takes to reduce your pain and allow you to self-manage.
- PAIN MANAGEMENT:
- Trial heat to address pain or contrast bathes if experiencing swelling and pain. For contrast bathes, soak your hand and wrist in warm water for 1-2 minutes, then switch to cool water x 1-2 minutes. Alternate between the two, ending with the cool water.
- RANGE OF MOTION:
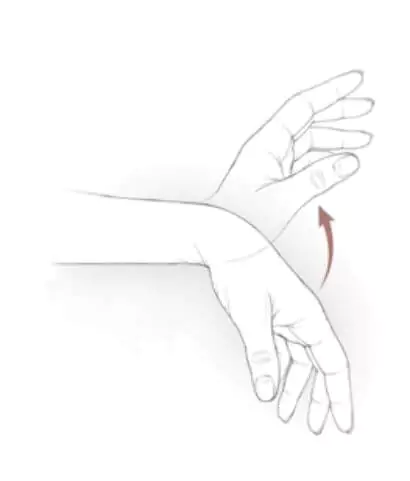
- Perform gentle wrist flexion and extension. Bend your wrist forward and back, leaving your fingers relaxed. You should feel a mild stretch, no pain.
- STRETCHES:
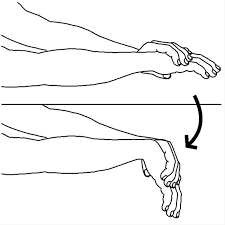
- Forearm extensor stretch: Curl your fingers into a fist, then flex your wrist (bend palm side downward) until you feel a mild stretch on the top side of your forearm. The goal is to stretch but not create pain.
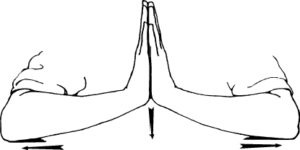
- Forearm flexor ‘prayer’ stretch: Place the palms of your hands together with fingers straight with hands positioned at chin height, then slowly move hands down towards chest level as you raise the elbow toward the ceiling to increase wrist extension (backward bend). The goal is to stretch but not create pain.
- ACTIVITY MODIFICATION:
- Pay attention to what activities increase your pain and consider how you might adapt the activity by improving your ergonomics or using adaptive tools to reduce wrist strain.
At Rose City Physical Therapy and Hand Therapy Specialists, our hand therapists will evaluate your condition and provide individualized treatment to help reduce your pain and return to your normal function. Treatment interventions may include therapeutic exercise, functional task-simulated activity, manual therapy, taping, pain and edema management, education on activity adaptations and ergonomics, and therapeutic modalities as appropriate.
Click here to download our FREE eBook on computer workstation ergonomics for a self-help checklist to ensure your computer workstation is correct to minimize repetitive strain injury.